| 6.1 |
Generation of Electricity |
Energy sources:
|
Energy source
|
Features
|
|
Renewable energy sources
|
-
Unlimited resources
-
Examples are geothermal, hydro, wave, wind, biomass, and solar energy
|
|
Non-renewable energy sources
|
-
Limited resources
-
For example, nuclear energy, petroleum, coal, and natural gas
|
Electricity generation:
-
Electrical energy is generated through the process of electromagnetic induction
-
Electricity is produced when the magnetic field is cut off and the current produced is called the induced current
-
Electricity can be generated by 5 types of generators, namely thermal electric generators, hydro electric generators, diesel-electric generators, gas turbine electric generators, and nuclear electric generators
The structure of thermal electricity generator:

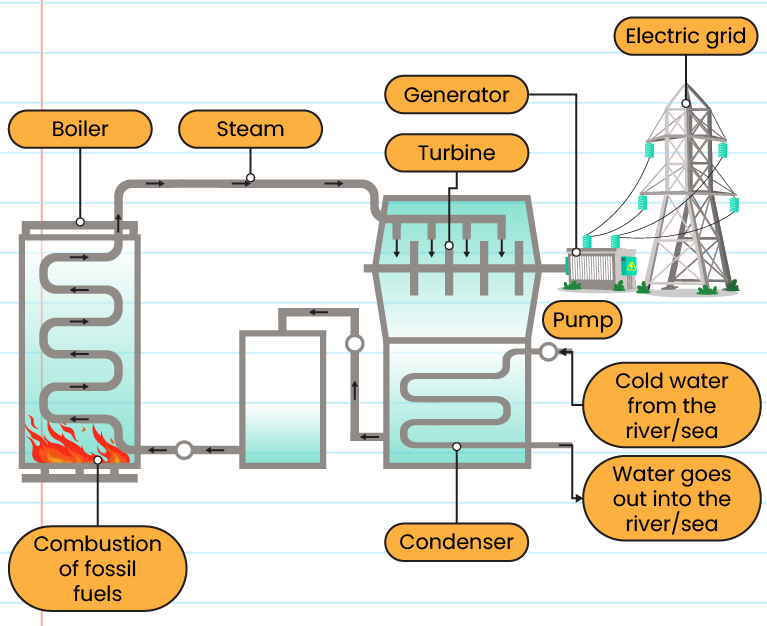
-
Using petroleum, natural gas, or coal as an energy source
-
Fuel is burned to boil water so that steam is produced
-
High-pressure steam is used to spin the turbine
-
The rotation of the turbine causes electrical energy to be generated by the dynamo
Hydroelectric generator structure:

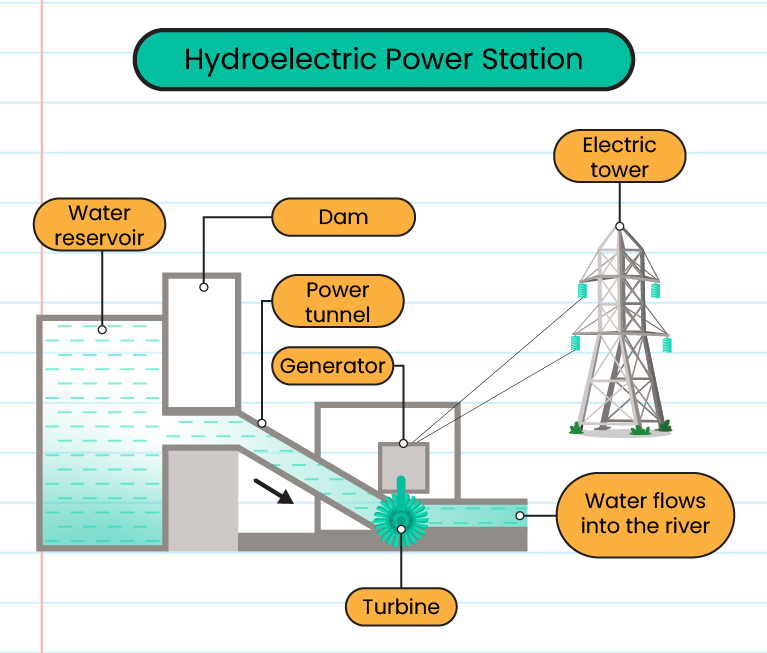
-
Using water boiled in dams to generate electricity
-
Water collected in high areas is channeled to generators located in low areas
-
The flow of water rotates the turbine and the movement of the dynamo generates electrical energy
Diesel-electric generator structure:

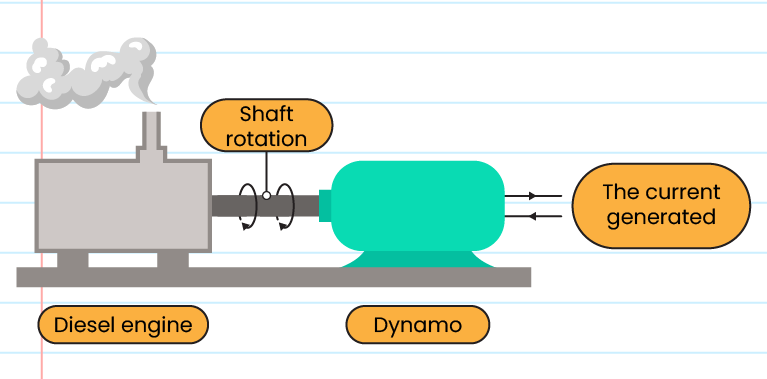
-
Uses diesel oil to run the engine which will spin the dynamo
-
A mixture of diesel and compressed air produces hot gas and then rotates a turbine to drive a dynamo and electricity is produced
Gas turbine electric generator structure:

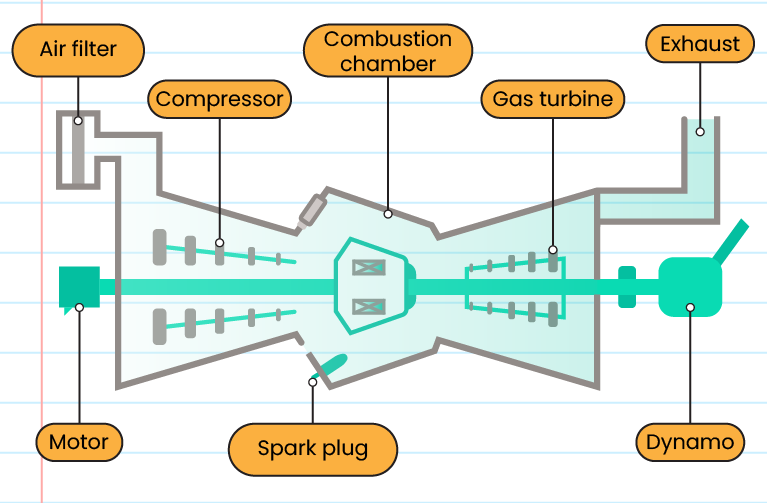
The structure of a nuclear power generator:

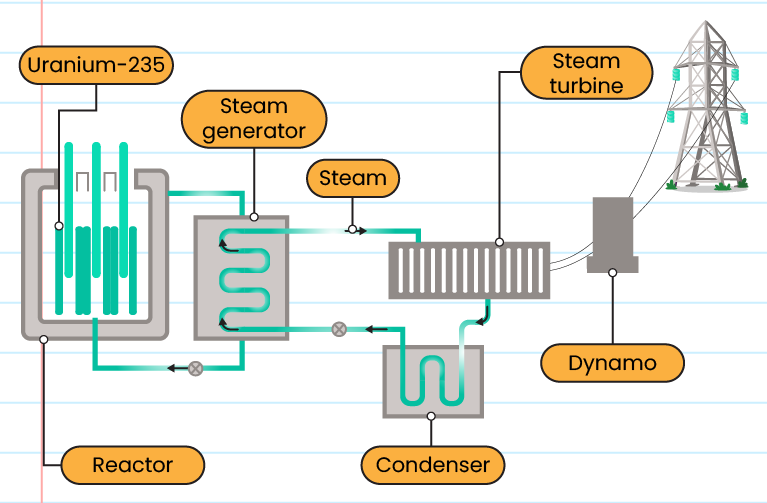
-
Using radioactive materials such as uranium as fuel
-
Nuclear reactions release a lot of heat and are used to boil water
-
Water produces steam and steam under high pressure rotates a turbine that drives a dynamo to generate electricity
Electric current:
-
Electric current is divided into direct current (d.c.) and alternating current (a.c.)
-
A cathode-ray oscilloscope is an electronic device used to show the shape of voltage versus time graphs for direct current and alternating current
Comparison of direct current and alternating current:
| |
Direct current (d.c.)
|
Alternating current (a.c.)
|
|
Directions
|
One direction only
|
Varies with time
|
|
Voltage value
|
Still
|
Changeable
|
|
Source
|
Solar cells and batteries
|
Most electric power generators
|
Solve problems related to electricity supply in life:
-
In some rural areas, there is still no electricity supply due to the high cost of building electricity generators or installing mains and the solution is to build hydroelectric generators in rivers
-
In highlands or windy open lands, electric generators such as windmills can solve the problem of electricity supply
Example question:
The diagram shows two types of energy sources.

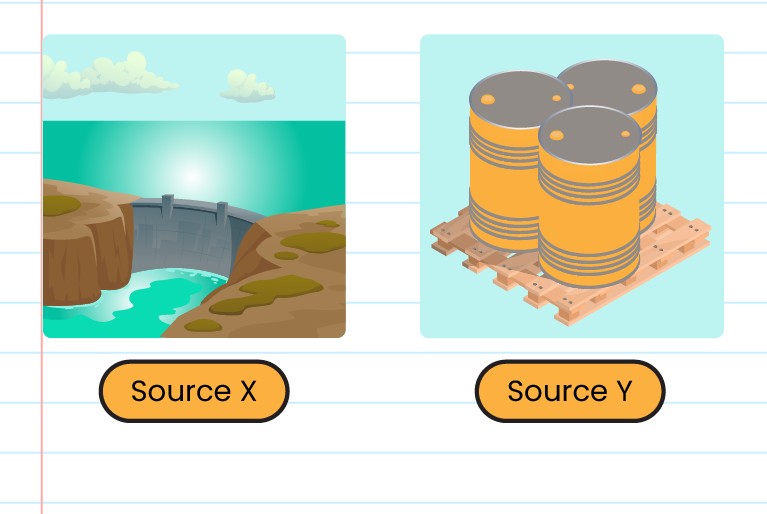
a) Which source is renewable and non-renewable energy sources?
b) Give one disadvantages of using electricity of source X and source Y?
Answer:
a) Source X is renewable energy source and Source Y is non-renewable energy source.
b) Disadvantages of using electricity of source X:
The construction of dams to generate electricity requires a large area and its construction will cause the destruction of the natural habitats of various types of organisms.
Disadvantages of using electricity of source Y:
The burning of fossil fuels releases various types of gases that pollute the air and cause the greenhouse effect.