| |
| 3. Addition of Water (Hydration) |
- Alkenes react with water (in the form of steam) at high temperature and pressure, in the presence of phosphoric acid, H3 PO4 as a catalyst to produce alcohol.
- Catalyst: phosphoric acid.
- Temperature: 300°C.
- Pressure: 60 atm.
- This reaction is also called the hydration reaction.
- Product: Alcohol.
\(\,\\C_2H_4(g) + H_2O(ce) \xrightarrow []{H_3PO_4}C_2H_5OH(ce)\)
|
| 4. Acidified potassium manganate(VII) solution, KMnO4 |
- Acidified potassium manganate(VII) solution is a very good oxidising agent.
- This reaction is also called the oxidation reaction.
- Product: Diol (Alcohol with two hydroxyl groups).
\(C_2H_4(g) + H_2O(l) \xrightarrow []{[O]} CH_2OHCH_2OH(l)\)
|
|
- The pair of electrons making up one of the double bonds is shared with the carbon atom of another alkene molecule in the polymerisation reaction.
- Example: polymerisation of ethene:
- Polymer: polyethene.
- Monomer: ethene.
- Pressure: 2000 atm.
- Temperature: 100°C to 300°C.
|
|
| |
| Penyediaan Etanol |
| Production of Ethanol in the Indutry |
- Addition reaction with water (steam)
- Catalyst: phosphoric acid.
- Temperature: 300°C.
- Pressure: 60 atm.
- \(C_2H_4(g) + H_2O(l) \xrightarrow[]{H_3PO_4} C_2H_5OH(l)\)
|
| Production of Ethanol in the Laboratory |
- The fermentation process of carbohydrate or sugary substances like rice, barley or fruits
- These substances contain glucose.
- Zymase in yeast acts as a catalyst to convert glucose to ethanol.
-
- \(C_6H_{12}O_6(aq) \xrightarrow[]{yis} 2C_2H_5OH(l) + 2CO_2(g)\)
|
|
| |
| Chemical Properties of Ethanol |
- Combustion of ethanol in excess oxygen produces carbon dioxide and water.
- \(C_2H_5OH(l) + 3O_2 (g) \rightarrow 2CO_2(g) + 3H_2O(l)\)
|
- Ethanol is oxidised by acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution.
- Product: ethanoic acid
- Dichromate ion (orange) changes to chromium ion (green).
- \(C_2H_5OH(l) \xrightarrow[]{[O]} CH_3COOH(l)\)
|
- A water molecule is eliminated from the reaction.
- Catalyst: sulphuric acid.
- Temperature: 180°C.
- Product: ethene.
- \(C_2H_5OH(l) \xrightarrow[]{H_2SO_4, 180^\circ C} C_2H_4(g) + H_2O(l)\)
|
|
| |
| Preparation of Ethanoic Acid in the Laboratory |
- Oxidation of ethanol
- Ethanol is oxidised by acidified potassium dichromate(VI) solution.
- Dichromate ion (orange) changes to chromium ion (green).
- \(C_2H_5OH(l) \xrightarrow[]{[O]} CH_3COOH (l)\)
|
|
| |
| Chemical Reactions of Ethanoic Acid as An Acid |
| Reaction with Base or Alkali |
- Product: salt and water
- Also known as neutralisation reaction.
- Example of reaction with sodium hydroxide:
- \(CH_3COOH (aq) + NaOH(aq) \rightarrow CH_3COONa (aq) + H_2O(l)\)
|
| Reaction with Reactive Metal |
- Product: salt and hydrogen gas
- Example of reaction with magnesium:
- \(2CH_3COOH (aq) + Mg(s) \rightarrow (CH_3COO)_2Mg (aq) + H_2(g)\)
|
| Reaction with Metal Carbonate |
- Product: salt, carbon dioxide gas and water
- Example of reaction with calcium carbonate:
- \(2CH_3COOH (aq) + CaCO_3(s) \rightarrow (CH_3COO)_2Ca(aq) + H_2O(l) + CO_2(g)\)
|
|
| |
| The Chemical Reaction of Ethanoic Acid with An Alcohol |
- Product: ester.
- Also known as an esterification reaction.
- Catalyst: hydrogen ion.
- \(CH_3COOH (aq) + C_2H_5OH(l) \xrightarrow []{H^+}CH_3COOC_2H_5(aq) + H_2O(l)\)
|
|
| |
| Ester |
- Functional group: carboxylate group, \(-COOC-\)
- General formula: \(C_nH_{2n+1}COOC_mH_{2m+1}\), where n = 0,1,2,… and m = 1,2,3,…
|
|
| |
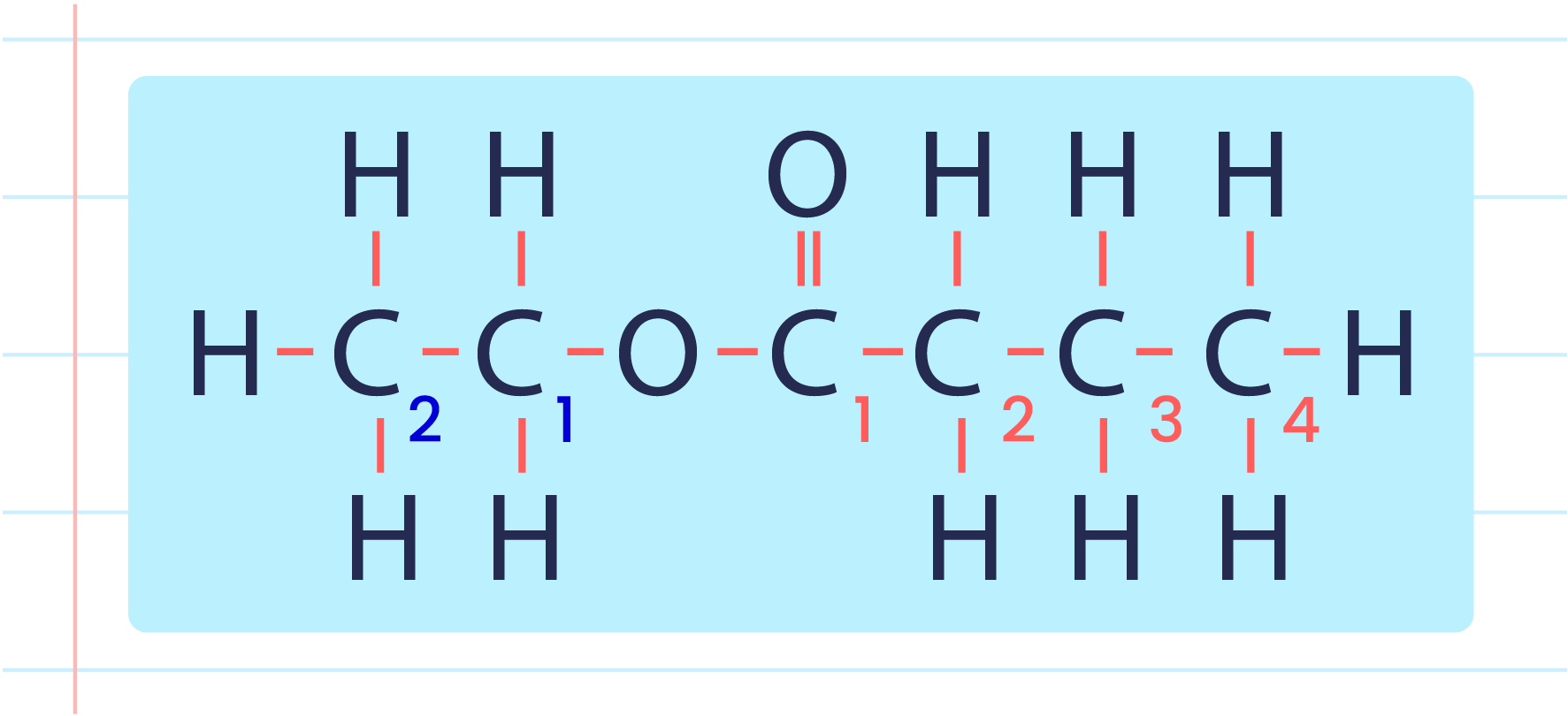
| Naming Ester |
- Ester is produced by combining alcohol with carboxylic acid.
- There are two parts to naming an ester.
- The first part is based on the name of the alcohol.
- The second part is based on the name of the carboxylic acid.
- Example: Ethyl butanoate.
|
|
| |
| Steps in Naming An Ester |
- Determine the alkyl group of the alcohol chain based on the structural formula or the molecular formula.
- Determine the name of the carboxylic acid part.
- Change the term ‘oic’ in carboxylic acid to ‘oate’.
|
|
| |
| Preparation of Ethyl Ethanoate in Laboratory |
- Mixing ethanoic acid with ethanol by reflux reaction.
- Reflux is needed because ethanol is a volatile solution.
- \(CH_3COOH(aq)+ C_2H_5OH(aq) \xrightarrow[]{ H_2SO_4} CH_3COOC_2H_5(aq)+H_2O(l)\)
|
|
| |
| Physical Properties of Ethyl Ethanoate |
- A colourless solution at room temperature.
- Nice fruity smell.
- Soluble in water.
|
|
| |
| Esterification Ester |
- Product: ester.
- Also known as an esterification reaction.
- Catalyst: hydrogen ion.
- Example of esterification reaction of ethanoic acid with ethanol:
- \(CH_3COOH(aq)+ C_2H_5OH(aq) \xrightarrow[]{ H_2SO_4} CH_3COOC_2H_5(aq)+H_2O(l)\)
|
|
| |
 |
| |
| Natural Sources of Ester |
| Flower or Fruit |
Ester |
|
Jasmie
|
Benzyl ethanoate |
|
Pear
|
Propyl ethanoate |
|
Apricot
|
Pentyl propanoate |
|
Kiwi
|
Methyl benzoate |
|
Pineapple
|
Ethyl butanoate |
|
Banana
|
3-methylbutyl ethanoate |
|
| |