| 5.2 |
Three States of Matter |
- Matter exists in three states, which are the solid, liquid or gaseous states.
- The arrangement of the particles in matter determines the state of matter whether it is solid, liquid or gas.
- The change of state of matter involves absorption or release of heat.
| State of matter |
Solid |
| Shape |
Fixed |
| Mass |
Fixed |
| Volume |
Fixed |
| Compressibility |
Incompressible |
| Space between particles |
Small |
| Particles arrangement |
Very close |
| Particles movement |
Vibrate in a fixed a position |
| State of matter |
Liquid |
| Shape |
|
| Mass |
Fixed |
| Volume |
Fixed |
| Compressibility |
Difficult to compress |
| Space between particles |
Moderate |
| Particles arrangement |
Close |
| Particles movement |
Move freely
and collide with one another
|
| State of matter |
Gas |
| Shape |
Take the shape of the container |
| Mass |
No fixed |
| Volume |
Followe the volume of the container |
| Compressibility |
Compressible |
| Space between particles |
Large |
| Particles arrangement |
Very loose |
| Particles movement |
Move randomly
and collide with one another
|
Diffusion Rate in Three States of Matter
| The rate of diffusion of particles in a solid, liquid and gas |
|
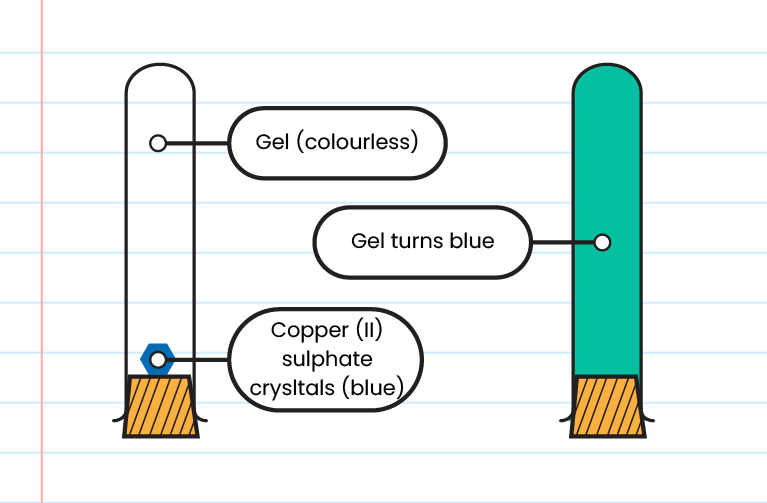
Solid
- The gel turns blue after a few days
- The rate of diffusion of particles in a solid is lo
|
 |
| |
|
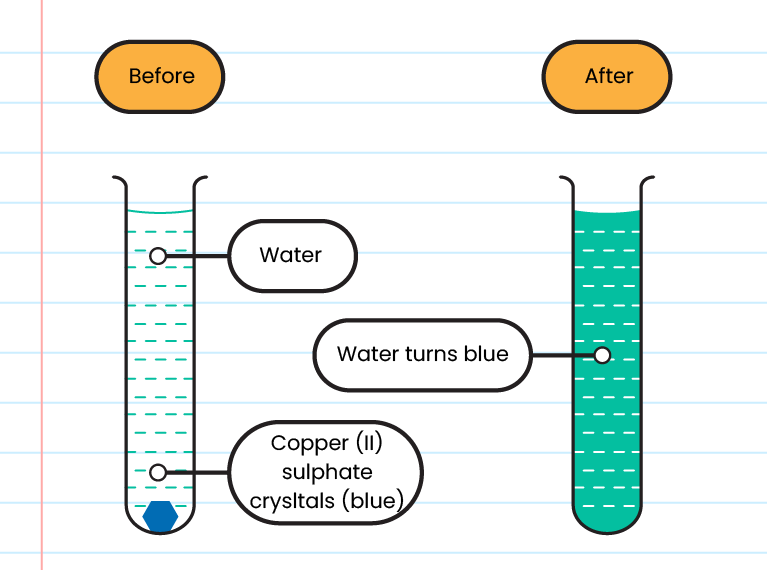
Liquid
- Water turns blue after two hours
- The rate of diffusion of particles in a liquid is higher than in solid
|
 |
| |
|
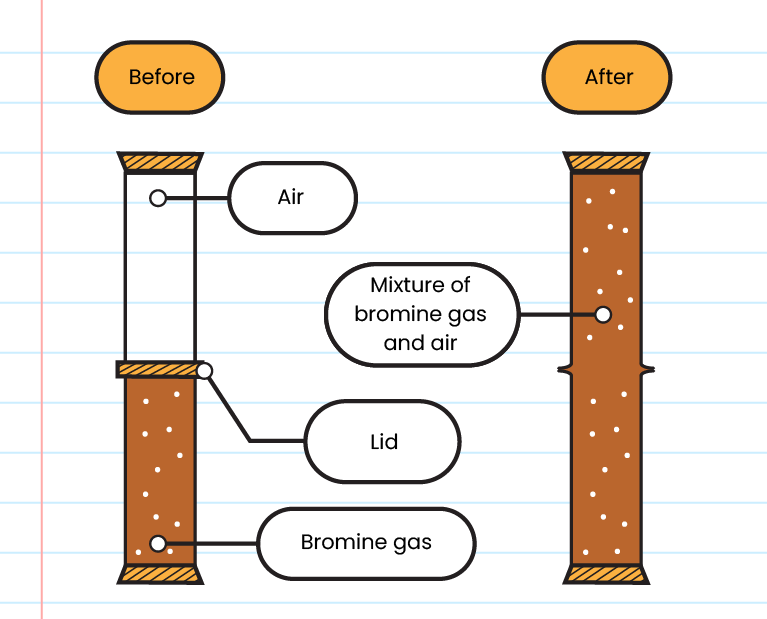
Gas
- Bromine gas fills both gas jars after 15 minutes
- The rate of diffusion of particles in a gas is the highest
|
 |
Examples of change of state of matter
- Water from wet items evaporates and becomes vapour through the process of evaporation
- Freezing allows sweet creams to freeze and become ice-cream
- Dry ice is used by ice-cream vendors to prevent their ice-cream from melting