| 8. 3 |
Ionising and Non-ionising Radiation |
|
Ionising radiation
|
Non-ionising radiation
|
|
- Ionising radiation contains a higher energy content and causes electrons to be released from the atoms or molecules it irradiates
- Examples of ionising radiation are alpha radiation, beta radiation, and gamma radiation
|
- Non-ionising radiation has a lower energy content and cannot release electrons from the atoms or molecules it illuminates
- Examples of non-ionising radiation are radio waves, microwaves, and infrared
|
The characteristics of alpha, beta, and gamma rays:
|
Characteristics
|
Alpha (α)
|
|
Particle size
|
Big
|
|
Charge
|
Positive
|
|
Ionising power
|
High
|
|
Penetrating power
|
Low
|
|
Deflection by magnetic fields
|
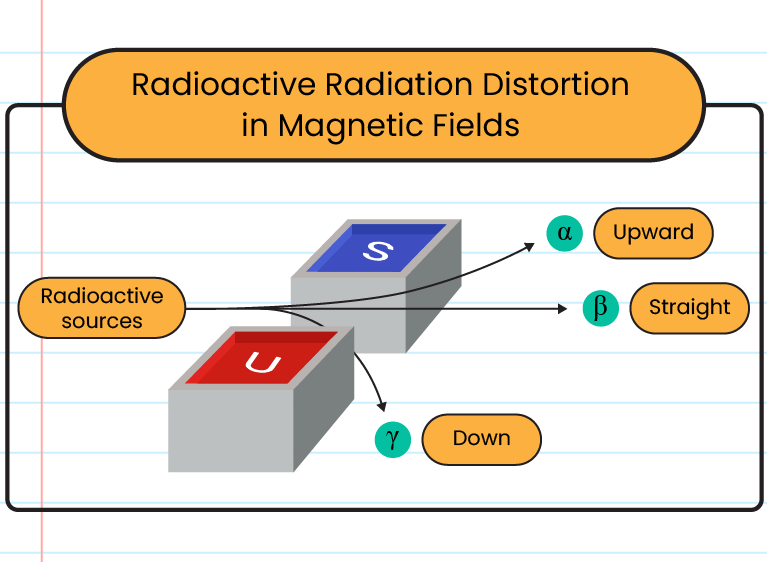  |
|
Deflection by an electric field
|
 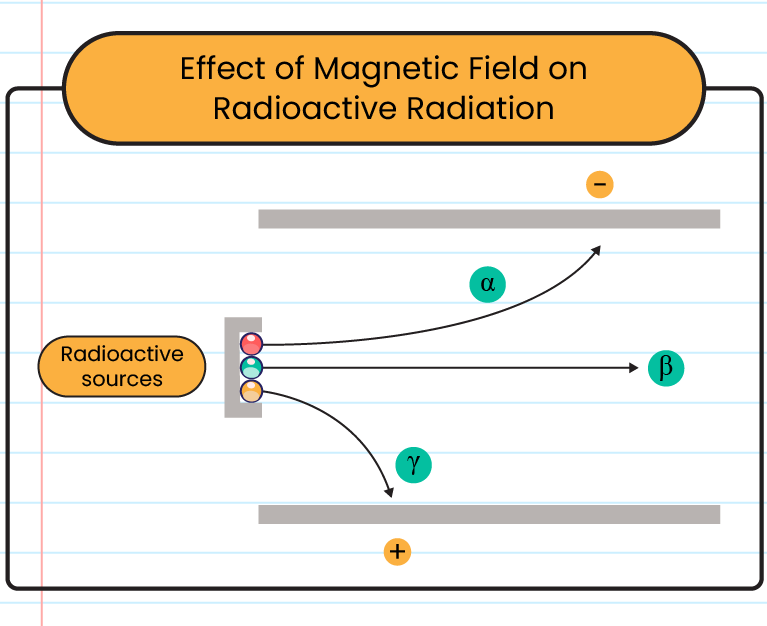 |
|
Beta (β)
|
Gamma (γ)
|
|
Small
|
None
|
|
Negative
|
Neutral
|
|
Medium
|
Low
|
|
Medium
|
High
|
Sources of ionising radiation:
-
Sources of ionising radiation are divided into natural sources and man-made sources
-
Sources of natural ionising radiation include cosmic radiation and background radiation
-
Cosmic radiation is radiation emitted continuously from outer space that can cause interference with weather and communication systems
-
Background radiation is radiation that is present everywhere but the level varies due to solar radiation and the presence of radon-222 gas (radioactive gas in the air)
-
Measured in microSievert units/hour (µSv/h)
-
Nuclear test and nuclear accident at Chernobyl April 1986 is a source of man-made ionising radiation
Exposure to ionising radiation and safety measures:
|
Radioactive effects
|
Security measures
|
|
- Destruction of cells or tissues in the body
- Genetic mutations that may cause tumor growth and cancer
- Infertility
- The skin burns and becomes blind
- Limb deformity and death for severe cases
|
- Chopsticks should be used to hold and transfer radioactive sources
- Radioactive material should be stored in lead containers
- Workers in radioactive laboratories must wear radioactive warning badges and special protective clothing made of lead rubber
- Lead shields can be used to protect users from radioactive radiation
- Radioactive waste must be handled properly so that it is safer and does not cause environmental pollution
|