| Definition |
|
Human blood consists of two components, namely 55% blood plasma (pale yellow fluid) and 45% blood cells (red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets)
|
The structure and function of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets:

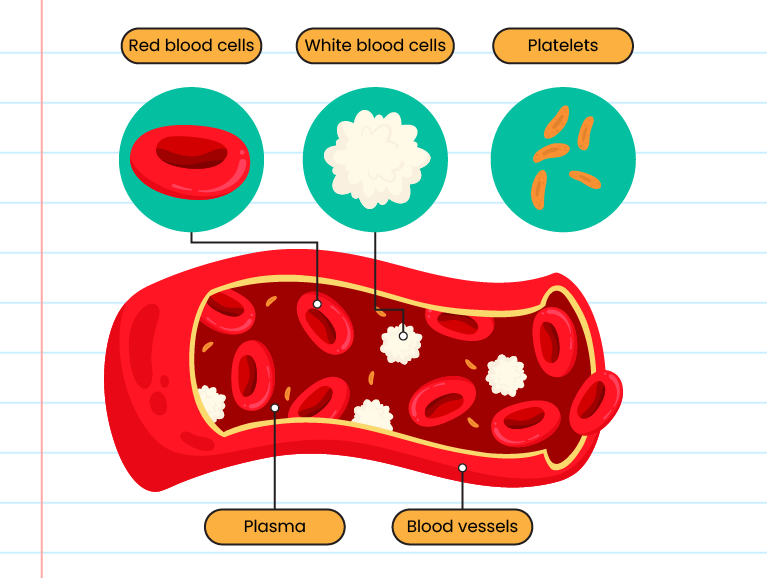
The chemicals and their functions:
|
Chemical substance
|
Function
|
|
Water
|
Water becomes a transport medium and solvent for respiratory gases, ions, digestive products, and excrement
|
|
Nutrients (glucose and vitamins)
|
Nutrients are important in energy production, growth, and health maintenance
|
|
Dissolved gas
|
Oxygen is used in cellular respiration and carbon dioxide is the result of cellular respiration
|
|
Wastes substances
|
Wastes such as urea are transported to the kidneys for elimination
|
|
Enzymes
|
Enzymes are needed to speed up biochemical reactions in cells
|
|
Hormones
|
Hormones are chemicals that regulate the activity of certain tissues or organs
|
The blood group and suitability of blood reception:

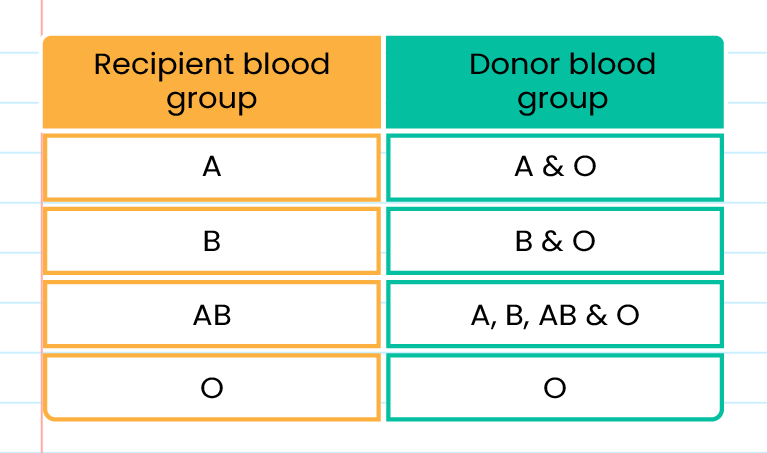
-
Blood group O is known as the universal donor while blood group AB is known as the universal recipient
-
Blood transfusion/blood transfusion should be done according to the appropriate blood class to prevent blood collection to the recipient
The importance of donating blood: